# Create mailbox to all users in a CSV based on the 3+3 naming policy.
# This will also create the user in AD
$parentcontainer = "contoso.com/container"
$homedirectory = "contoso.comusers$username"
# Prompt the user for password
$password = Read-Host "Enter password" -AsSecureString
# The following has to be done to import with european characters
cat "c:tempusers.csv" > c:templisttemp.csv
# Loop through the list and
# - replace european letters with o,a or e.
# - create username based on the 3+3 naming convention
# (three first letters in the firstname and lastname.)
# - all lower case
import-csv c:templisttemp.csv | foreach {
$username = ($_.firstname.substring(0,3) + $_.lastname.substring(0,3)).tolower()
$username = $username.replace("ø","o")
$username = $username.replace("å","a")
$username = $username.replace("æ","e")
# The following line can create the user if you do not need mailbox.
# new-qadUser -ParentContainer $parentcontainer -FirstName $_.firstname -LastName $_.lastname -DisplayName $($_.FirstName + " " + $_.LastName) -SamAccountName $username -Name $username -UserPrincipalName ($username + '@contoso.com') -whatif
# Create the mailbox
New-Mailbox -Alias $username -Name $($_.FirstName + " " + $_.LastName) -OrganizationalUnit $parentcontainer -UserPrincipalName ($username + '@contoso.com') -SamAccountName $username -FirstName $_.firstname -LastName $_.lastname -ResetPasswordOnNextLogon $false -password $password -whatif
}
Author Archives: suneworld
Adding snapins/modules to PowerShell
# Import the ActiveDirectory cmdlets Import-Module ActiveDirectory # List available snapins on your system: Get-PSSnapin # List registered snapins Get-PSSnapin -Registered # Alias: gsnp # Add Snapin: Add-PSSnapin # Examples: Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.Admin # Exchange 2007 Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.E2010 # Exchange 2010 Add-PSSnapin Microsoft.SystemCenter.VirtualMachineManager # WMM (Hyper-V) Add-PSSnapin Quest.Activeroles.ADManagement # Quest commandlets
(You can download the Quest Commandlets from <a href="# Install from http://www.quest.com/powershell/activeroles-server.aspx” title=”# Install from http://www.quest.com/powershell/activeroles-server.aspx“>here.)
You will get an error if you try to add a snapin that is already added. Your script will continue to run but you’ll have a bunch of nasty red letters in your shell. Not too sexy, eh? The way to avoid this is to first check if the snapin is loaded and then only load if it is not.
Do it like this:
# Add Exchange 2007 commandlets (if not added)
if(!(Get-PSSnapin |
Where-Object {$_.name -eq "Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.Admin"})) {
ADD-PSSnapin Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.Admin
}
# Add Exchange 2010 commandlets (if not added)
if(!(Get-PSSnapin |
Where-Object {$_.name -eq "Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.E2010"})) {
ADD-PSSnapin Microsoft.Exchange.Management.PowerShell.E2010
}
# Add Virtual Machine Manager (Hyper-V) commandlets (if not added)
if(!(Get-PSSnapin |
Where-Object {$_.name -eq "Microsoft.SystemCenter.VirtualMachineManager"})) {
ADD-PSSnapin Microsoft.SystemCenter.VirtualMachineManager
}
# Add Quest commandlets (if not added)
if(!(Get-PSSnapin |
Where-Object {$_.name -eq "Quest.Activeroles.ADManagement"})) {
ADD-PSSnapin Quest.Activeroles.ADManagement
}
Head on over to http://blogs.technet.com/b/heyscriptingguy/archive/2010/10/16/learn-how-to-load-and-use-powershell-snap-ins.aspx to learn more about snapins.
Launching remote desktop from the command line
The remote desktop connection dialog box provides you with everything that you need to configure and connect to another computer capable of RDP. You can use the Save As button on the Connection Settings panel to save all your connection settings as an RDP file. Then, you can launch and connect to a remote computer simply by double-clicking the RDP file.
You can also script a remote desktop connection. The remote desktop connection executable file is MSTSC.EXE, and the following are some of the most common parameters:
- /v:<computername>–specifies the name of the computer to connect to.
- /f–starts the connection in a full screen.
- /w:<width>–specifies the width of the remote desktop screen.
- /h:<height>–specifies the height of the remote desktop screen.
- /admin – connects with admin rights
- /console – connects to the console of a Windows Server 2003 based system
For example, to remotely connect to a computer named Kaltec in a 640 x 480 remote desktop screen, you would use the following command:
mstsc /v: Kaltec /w:640 /h:480
You can type this command line in the Run dialog box, as well as use it in a batch file.
mstsc.exe {ConnectionFile | /v:ServerName[:Port]} [/console] [/f] [/w:Width/h:Height]
Display size of cluster shared volumes
Import-Module FailoverClusters
$objs = @()
$csvs = Get-ClusterSharedVolume
foreach ( $csv in $csvs )
{
$csvinfos = $csv | select -Property Name -ExpandProperty SharedVolumeInfo
foreach ( $csvinfo in $csvinfos )
{
$obj = New-Object PSObject -Property @{
Name = $csv.Name
Path = $csvinfo.FriendlyVolumeName
Size = $csvinfo.Partition.Size
FreeSpace = $csvinfo.Partition.FreeSpace
UsedSpace = $csvinfo.Partition.UsedSpace
PercentFree = $csvinfo.Partition.PercentFree
}
$objs += $obj
}
}
$objs | ft -auto Name,Path,@{ Label = "Size(GB)" ; Expression = { "{0:N2}" -f ($_.Size/1024/1024/1024) } },@{ Label = "FreeSpace(GB)" ; Expression = { "{0:N2}" -f ($_.FreeSpace/1024/1024/1024) } },@{ Label = "UsedSpace(GB)" ; Expression = { "{0:N2}" -f ($_.UsedSpace/1024/1024/1024) } },@{ Label = "PercentFree" ; Expression = { "{0:N2}" -f ($_.PercentFree) } }
Last logged on time of a user
Get-QADUser "UserName" |
Format-Table -Property @{Label='LastLogonLocal';Expression={$_.lastLogon.ToLocalTime()}}
(Requires Quest AD cmdlets)
Check size of users mailbox and sort on size on a specific database
Get-MailboxStatistics -Database "YOURDATABASE" |
Sort-Object TotalItemSize –Descending |
ft @{label=”User”;expression={$_.DisplayName}},@{label="Total Size (MB)";expression={$_.TotalItemSize.Value.ToMB()}},@{label=”Items”;expression={$_.ItemCount}},Database
Hide contact from Global Addresslist (GAL)
get-mailcontact "yourcontact" | Set-mailContact -HiddenFromAddressListsEnabled $true
WebExplorer
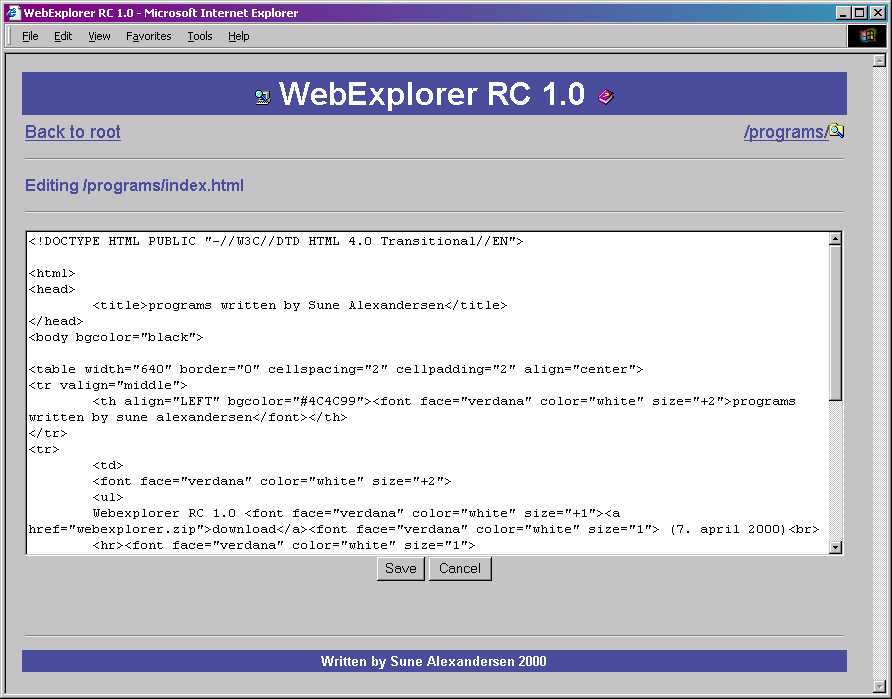
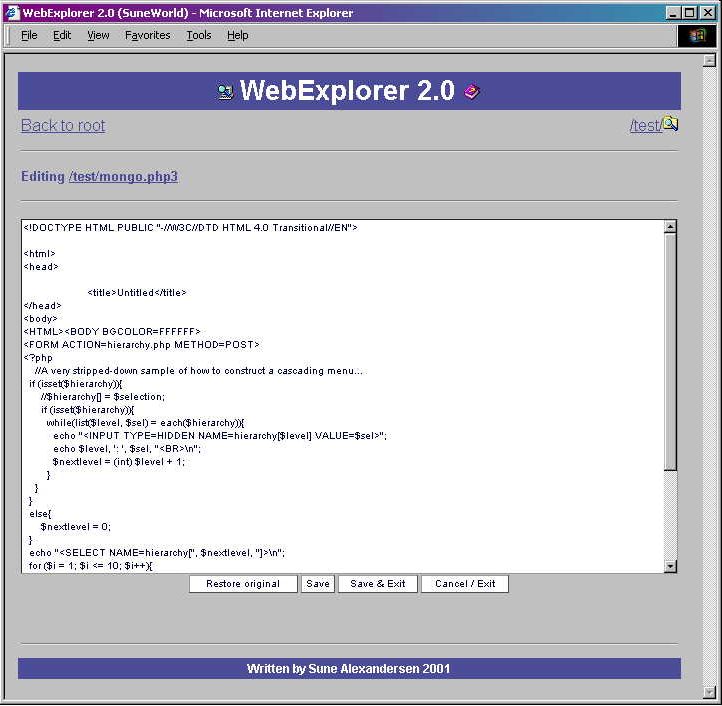
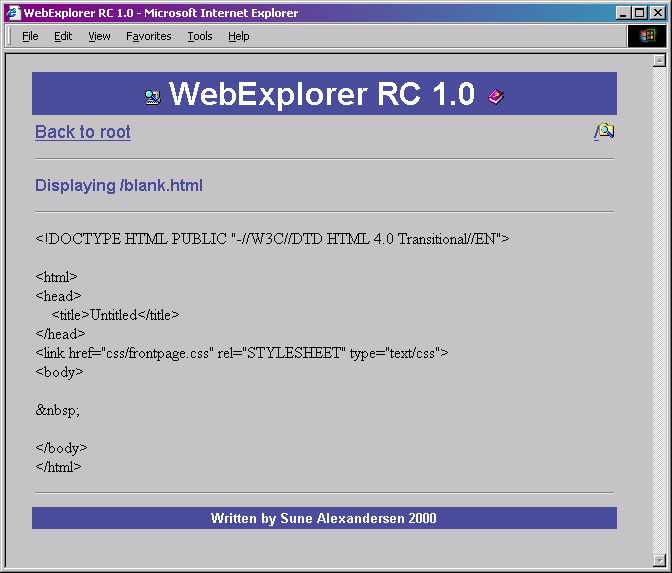
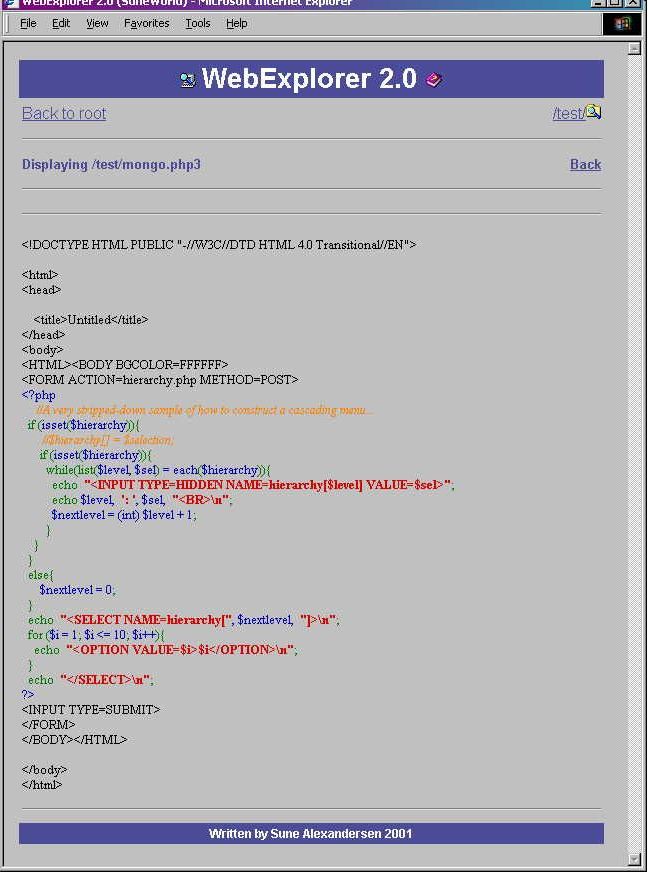
WebExplorer is a Windows Explorer style file manager through your webbrowser, but don’t let the “Windows part” of it scare you away! Just upload the file to your designated “admin” directory on your PHP enabled website, edit the variable $basedir to reflect your website, and off you go!!
This application lets you edit, browse, CHMOD, view, move, rename, copy, and create files/directories in any forms/tables enabled browser. You even have the option to create html skeleton-files.
I haven’t done any work on WebExplorer since 2002 so it can be considered abandonware. But feel free to use.
What does WebExplorer require?
Webserver with PHP3 or newer installed
How about security?
WebExplorer does not have any “built in” authorization function. Use HTAccess or similar for this.
Can you develop blah blah or make WebExplorer do yaddayadda?
Donate first, ask later.
Do you support WebExplorer?
See previous q/a
How many downloads?
Lost track a long time ago… I’d guess around 35 000.
Download
webexplorer20.zip
webexplorer20.tar.gz
Disable email addresspolicy on all contacts in one OU
Get-mailcontact -OrganizationalUnit "contoso.com/path/to/ou" | Set-mailContact -EmailAddressPolicyEnabled $false -whatif
Hide all contacts in one OU from addresslist
get-mailcontact -OrganizationalUnit "contoso.com/path/to/ou" | Set-mailContact -HiddenFromAddressListsEnabled $true -whatif